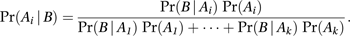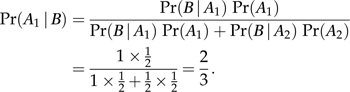Craig uses probability calculus to attempt to refute Ehrman’s claim that historians “cannot say that the explanation which is inherently the most improbable is probable” (whether or not he succeeded is up to you). For a summary of Ehrman's argument against the resurrection, see: http://honestsearchfortruth.blogspot.com/2011/09/can-miracle-ever-be-best-explanation.html
In the debate, Craig had severe time limitations and could not explain the probability calculus he used enough for most people to understand what the heck he was talking about. Out here in the real world, however, we have as much time as we would like! This means that I will be spending my Saturday morning learning about and explaining the relevant topics in probability calculus for you. This is necessary if we want to make a decision as to whether Craig, Ehrman, or neither of them is correct on the historicity resurrection! To know whether or not Jesus rose from the dead, you need to know a little probability calculus.
I promise that I will only share the math that is absolutely necessary for understanding! Don’t be intimidated by the subject material of this post- it is pretty easy if you attack it with patience and confidence!
In addition, if promise to help anyone who is willing to learn with this topic! Comment, email, call, or coffee!
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
**But first, thank you to science.jrank.org!!! (the website from which I obtained my knowledge) <a href="http://science.jrank.org/pages/51901/prior-probability.html">prior probability</a>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Here are two kinds of probabilities: A prior probability and a posterior probability.
- Prior probability- “The probability attached to an event before certain data are obtained.”
- Posterior probability- “the probability attached to it after the data are obtained.”
Because the information on the resurrection of Jesus has already been obtained, we are looking at a posterior probability.
To find a posterior probability, we use Baye’s Theorem:
Don’t get intimidated by this big equation! There is a simple way to break it down.
Pr(Ai|B) is the thing we are trying to find. It is the probability of an event, (Ai), happening with respect to other events B. A1 is one event, A2 is another event, A3 is another event, and we can just keep on adding as many events as we want. The total number of events we have in our probability is equal to K.
The best way to explain this will be to use an example. We will make it simple- only two events- A
1 and A
2.
- Let’s make A1 the tossing of a double sided coin- both sides are heads. We will call this coin “Coin X. ” The probability of getting ‘heads’ when tossing Coin X is 100%. Event probability: 100%.
- Let’s make A2 the tossing of a normal coin with heads on one side and tails on the other. We will call this coin “Coin Y.” The probability of getting ‘heads’ when tossing Coin Y is 50%. Event probability: 50%
Now, we are going to put the two coins into a bag, blindfold Larry, and ask him to pick one of the coins randomly from the bag. The probability that Larry will pick Coin X is 50%, and the probability that he will pick Coin Y is 50%.
Keep in mind that picking Coin X corresponds to the event “A
1.” Picking Coin Y corresponds to “A
2.”
The way to say that “the probability of Larry picking Coin 1 is 50%” is: Pr(A1)=1/2
The way to say that “the probability of Larry picking Coin 2 is 50%” is: Pr(A2)=1/2
Now, let’s make B the ‘event’ of obtaining heads after flipping the coin that Larry randomly selects.
- If Larry picks Coin 1, the probability of obtaining heads is 100%, or Pr(B|A1)=1
- If Larry picks Coin 2, the probability of obtaining heads is 50%, or Pr(B|A2)=1/2
We are reading to see the whole mathematical formula for our example.
What this mathematical thingy is saying is this:
“given that ‘heads’ was the outcome, the probability that it was the double-headed coin that was flipped is 2/3.” (science.jrank.org)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Know what I think it is time for? ANOTHER EXAMPLE!!!
Or rather, same example, but let’s do it where we are finding Pr(
A2|B) instead of Pr(
A1|B).
Summary of Heads Example:
Pr(A1) = 1/2
Pr(A2) = 1/2
Pr(B|A1) = 1
Pr(B|A2) = 1/2
So, given that ‘heads’ was obtained, what is the probability that it was Coin 2 that was tossed?
Here is the mathymajigger:
Pr(A2|B)= Pr(B|A2) Pr(A2)
Pr(B|A
2) Pr(A
2) + Pr(B|A
1) Pr(A
1)
Now we plug in our numbers:
Pr(A2|B)=
½ x ½
(½ x ½) + (1 x ½)
And after we do some fun math we come out with
Pr(A2|B)= 1/3
This means:
Given that ‘heads’ was obtained, the probability that it was Coin 2 that was tossed is 1/3.
From our first two examples, we now know that if the event that occurs is obtaining heads (or B=’the event of obtaining heads), that the probability that it was Coin 1 that was flipped is 2/3, and the probability that it was Coin 2 that was flipped is 1/3.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ok time for a break! NOT. TIME FOR ANOTHER EXAMPLE!!!
MUAHAHAHAHAAHAAAA!
It seems like I woke up this morning and thought “I wonder what blog post I could write to scare off the most people, give the highest number of people headaches, and discourage basically everyone to never read anything Josh writes again? Oh! I know! I’ll do an excruciatingly long post on PROBABILITY CALCULUS!!! And then I’ll give them… As many examples as they will need to actually understand what I’m saying...”
Anyway,iIf you are like me, you NEED this many examples to understand these principles.
In addition, IF YOU WANT TO KNOW WHETHER OR NOT IT IS PROBABLE THAT JESUS ROSE FROM THE DEAD, YOU NEED TO UNDERSTAND BAYE’S THEOREM. And I’m going to make it as easy as possible for you! I'm doing all the leg work!
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ok, same example as before, but we are going to make C the event of obtaining ‘tails’ instead of using B.
So,
given that ‘tails’ was obtained, what is the probability that it was Coin 1 that was tossed?
- Let’s make A1 the tossing of a double sided coin- both sides are heads. The probability of getting ‘tails’ when tossing Coin X is 0%. Event probability: 0%.
- Let’s make A2 the tossing of a normal coin with heads on one side and tails on the other. The probability of getting ‘tails' when tossing Coin Y is 50%. Event probability: 50%
----------------------------------
- The probability of Larry picking Coin 1 is 50%: Pr(A1)=1/2
- The probability of Larry picking Coin 2 is 50%: Pr(A2)=1/2
- If Larry picks Coin 1, the probability of obtaining tails is 0%, or Pr(C|A1)=0
- If Larry picks Coin 2, the probability of obtaining tails is 50%, or Pr(C|A2)=1/2
Summary of Tails Example:
Pr(A1) = 1/2
Pr(A2) = 1/2
Pr(B|A1) = 0
Pr(B|A2) = 1/2
Our mathematical thingy:
Pr(A
1|C)=
Pr(C|A1) Pr(A1)
Pr(C|A
1) Pr(A
1) + Pr(C|A
2) Pr(A
2)
Now we plug in the numbers:
Pr(A
1|C)=
0 x ½
(0 x ½) + (½ x ½)
This means:
Given that ‘tails’ was obtained, the probability that it was Coin 1 that was tossed is 0.
*This example is especially useful because you can use your intuition to find the answer without using math- ‘tails’ cannot be obtained from flipped a coin with heads on both sides. By relating your intuition to the math, you can increase your understanding of probabilities!
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
WHO’S READY FOR ONE MORE EXAMPLE? Well, I’ve only been studying, writing, and trying to make this crazy math stuff understandable for the past 6 hours of my Saturday morning. Might as well be thorough.
This last example should be ridiculously easy if you read the first three.
Same example, but let’s see what the probability of Coin 2 being tossed is if the result is ‘tails.'
Summary of Tails Example:
Pr(A1) = 1/2
Pr(A2) = 1/2
Pr(B|A1) = 0
Pr(B|A2) = 1/2
And the summary in english:
- The probability of Larry picking Coin 1 is 50%: Pr(A1)=1/2
- The probability of Larry picking Coin 2 is 50%: Pr(A2)=1/2
- If Larry picks Coin 1, the probability of obtaining tails is 0%, or Pr(C|A1)=0
- If Larry picks Coin 2, the probability of obtaining tails is 50%, or Pr(C|A2)=1/2
Pr(A
2|C)=
Pr(C|A2) Pr(A2)
Pr(C|A
2) Pr(A
2) + Pr(C|A
1) Pr(A
1)
Pr(A2|C)=
½ x ½
(½ x ½) + (0 x ½)
This means:
Given that ‘tails’ was obtained, the probability that it was Coin 1 that was tossed is 1 (or 100%).
If you managed to make it this far in this post, the next time I see you, I WILL give you a hug. If you don’t want to be hugged, just tell me that you didn’t read the last word or two. Otherwise I WILL hug you.
So, what does this have to do with the resurrection of Jesus? Check out my next post on Craig’s rebuttal of Ehrman’s argument against the resurrection of Jesus. Now that you are equipped with
‘the sword of probability calculus,’ you will be able to understand what the heck William Lane Craig is actually talking about!
For more analysis of probability, and a greater focus on the implications for the Craig-Ehrman debate, check out this post by
neo
the philosopher.